
"Buy line opeazitro, antibiotic vaginal itching".
By: Z. Fasim, M.A.S., M.D.
Co-Director, Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin
In pregnant women in areas where the disease is endemic in Latin America virus free music downloads generic 500 mg opeazitro free shipping, the seroprevalence of T infection in belly button discount 250mg opeazitro with visa. Two cases of treatment of Chagas disease in pregnancy with benzdidazole have been reported antibiotics made simple generic opeazitro 100mg fast delivery. However, the efficacy of this therapy is suboptimal, and treated patients are still at risk of reactivation. The oral transmission of Chagas’ disease: an acute form of infection responsible for regional outbreaks. Chagas disease: current epidemiological trends after the interruption of vectorial and transfusional transmission in the Southern Cone countries. Pathology of patients with Chagas’ disease and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Chagas’ disease in patients with kidney transplants: 7 years of experience 1989- 1996. Reactivation of Chagas’ disease in a human immunodeficiency virus- infected patient leading to severe heart disease with a late positive direct microscopic examination of the blood. Serologic testing for Trypanosoma cruzi: comparison of radioimmunoprecipitation assay with commercially available indirect immunofluorescence assay, indirect hemagglutination assay, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits. Use of a rapid test on umbilical cord blood to screen for Trypanosoma cruzi infection in pregnant women in Argentina, Bolivia, Honduras, and Mexico. Geographic variation in the sensitivity of recombinant antigen-based rapid tests for chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Comparison of the polymerase chain reaction with two classical parasitological methods for the diagnosis of Chagas disease in an endemic region of north-eastern Brazil. Early diagnosis of recurrence of Trypanosoma cruzi infection by polymerase chain reaction after heart transplantation of a chronic Chagas’ heart disease patient. Prevention of the transmission of Chagas’ disease with pyrethroid-impregnated materials. Evaluation and treatment of chagas disease in the United States: a systematic review. Toxic side effects of drugs used to treat Chagas’ disease (American trypanosomiasis). Successful treatment with posaconazole of a patient with chronic Chagas disease and systemic lupus erythematosus. Maternal Trypanosoma cruzi infection, pregnancy outcome, morbidity, and mortality of congenitally infected and non-infected newborns in Bolivia. Prevalence of antibody to Trypanosoma cruzi in pregnant Hispanic women in Houston. Mother-child transmission of Chagas disease: could coinfection with human immunodeficiency virus increase the risk? Thirteenfold increase of chromosomal aberrations non-randomly distributed in chagasic children treated with nifurtimox. Administration of benznidazole, a chemotherapeutic agent against Chagas disease, to pregnant rats. Uneventful benznidazole treatment of acute Chagas disease during pregnancy: a case report. On the basis of limited data, the maturation process is completed in approximately 1 to 2 days but might occur more rapidly in some settings.
GBL (Gamma Butyrolactone (Gbl)). Opeazitro.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96796
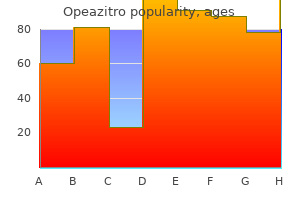
Such numbers are important to quantify economic impact and also to assess potential risk to source health systems antibiotic resistance cattle cheap opeazitro 250mg with amex. Clarification is required around the sources and surveys used to provide numbers antibiotic powder generic opeazitro 500mg line, including the role of national agencies and private facilities in providing numbers antibiotics mixed with alcohol purchase opeazitro with a mastercard. Extrapolating from a country to a more global perspective is difficult, as is ensuring ‗the count‘ is appropriate (do we count patients or treatment episodes; day treatments or in-stay treatment; expatriates and those funded by their multinational employers; only large and accredited providers? That many of the flows are confidential to protect privacy around treatments and choices makes the count further problematic. Such health trade is also not seen as a priority for measurement by national stakeholders. Different drivers may exist for higher and lower income patients groups travelling from North America and Western Europe. But we know relatively little about socio-demographic profile, age, gender, existing health conditions and status in attempting to map the composition of the medical tourism market. Medical tourists are likely to come from certain social and population groups and future research should seek to identify this social patterning, as it might increase inequality (cf Exworthy and Peckham, 2006). While there is a disagreement over the total number of medical tourists, figures are relatively consistent with regard to the costs of procedures. Ehrbeck et al (2008) note, however, that cost is not necessarily the main driver, suggesting that availability and quality are the major factors for many medical tourists. Drivers of medical tourism include globalisation – economic, social, cultural and technological. Many domestic health systems are undergoing significant challenges and strain – tightened eligibility criteria, waiting lists, and shifting priorities for health care may all impact on consumer decision making. There is also the emergence of patient choice and forms of consumerism, including within countries that traditionally have had public-funded services. Openness of information and development of diverse providers competing on quality and price now cater for all demands. Unlike other forms of patient mobility where decisions on behalf of the patient are made by an expert clinician (the agency relationship), medical tourism involves individuals acting as a consumer and making their own decisions regarding their health needs, how these can best be treated, and the most appropriate provider. They are therefore especially prone to well-known problems related to information asymmetry and provider-induced demand. Some treatments may not be available or may be subject to a wait in the home country. The desire for privacy and the wish to combine traditional tourist attractions, 15 hotels, climate, food, cultural visits with medical procedures are also thought to be key contributing factors to the growth in this market (see discussion in Connell, 2006, MacReady, 2007, Ramírez de Arellano, 2007). There is, however, little firm evidence on the relative importance of these different factors in influencing decisions to seek treatment abroad. There remains a dearth of empirical research; for example, there is little that adds to knowledge concerning the patient‘s decision to have domestic cosmetic treatments (Brown et al. We know relatively little about particular treatments and source/destination countries. If proximity is an important, but not a decisive, factor in shaping choices given peoples‘ ability and seeming willingness to travel longer distances there is a need for a greater understanding of how trade-offs are made and how these differ for different treatments and consumer groups (Exworthy and Peckham, 2006). Important questions remain with regard to how consumers assimilate and synthesise the information they retrieve from website searches, and how they take into account commercial interests and bias when making decisions. Again there is no research evidence around this dimension of medical tourism and this requires research investment, for example to know about patient understanding of risk. There is some evidence relating to how breast augmentation patients use the internet, with one survey suggesting that 68% of respondents utilized internet information, and of this subset of patients the information influenced decision making around the choice of procedures (in 53% of cases), choice of surgeon (36% of cases) and choice of hospital (25% of cases) (Losken et al.
Studies in animals or human beings have demonstrated fetal abnormalities bacteria glycerol stock purchase opeazitro now, or there is evidence of fetal risk based on human experience antibiotics you can drink on order opeazitro 500mg mastercard, or both antibiotic resistance youtube order opeazitro uk, and the risk of the use of the drug in pregnant women clearly outweighs any possible benefit. A dditionaldrugreceived byth ebabyth rough breastmilkincreasesth erisk ofadversedrug effects. Clofazimine: a review of its use in leprosy and Mycobacterium avium complex infections. Ciprofloxacin in pediatrics: worldwide clinical experience based on compassionate use-safety report. Prevention and Treatment of Tuberculosis among patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: principles of treatment and revised recommendations. Mycobacterium avium complex infection, rifabutin, and uveitis—is there a connection? A comparison of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, clarithromycin and cefixime examined by observational cohort studies. Tackling the burden of non-adherence requires a collaborative, patient- centric approach that considers individual patient needs and results in intelligent interventions that combine high-tech with high-touch. His • The emerging paradigm of patient centricity in doctor prescribed multiple meds: the critical insu- adherence. He takes out his Industry Dynamics Reshape pill box but wonders, “Should I take both doses Healthcare Delivery together or skip the frst one? Expected to account for three-fourths intriguing and complex of patient behaviors. Non- of all deaths globally by 2020 , chronic illness1 adherence to a therapeutic regimen can result is straining the healthcare capacity of many in negative outcomes, and it can be compound- countries that lack the resources to provide ed in populations with chronic illness because of adequate healthcare services. Industry interest in patient engagement has Non-adherence leads to One school of thought spiked, infuenced by the release in late August deteriorating health out- 2012 of the Meaningful Use Stage 2 Final Rule by postulates that instead comes across patient the U. Now that patient engagement is being mortality rates in dia- creating new medications called the biggest blockbuster drug of the century, betes and heart disease pharmaceuticals and healthcare industry players to cure chronic diseases, patients, non-adherers need to reconfgure their resources to develop applying a fraction of had much higher mortal- innovative business models that are based on val- ity rates (12. Its three tenets include improving the eases, applying a fraction of that cost to helping patient experience, improving population health patients adhere to their medications would actu- and reducing the per capita cost of healthcare. Kearney analysis Figure 1 Traditional Management of adherence in certain situations, but a “one-size- Non-adherence fts-all” approach is not effective; one-tool solutions often become marginalized if the pro- Conventional health models have historically gram does not address the underlying barriers placed patients with different health conditions of adherence. The traditional approach of designing programs Understanding the Causes of that address individual adherence barriers has Non-Adherence resulted in extremely siloed health management programs. These programs are less effective The reasons for patient non-adherence are because they don’t account for the fact that non- complex and multifactorial, and an effective adherence is caused by the presence of multiple coordinated care model needs to consider all of factors. Both internal factors (a taking their medication, and adherence rates patient’s intentional and unintentional beliefs) plummet, in just a few months, with 50% to 90% and external factors (those related to the health- of patients stopping their prescribed therapies by care system, family support, the therapy regimen, the end of the frst year of treatment (see Figure 1). All of these factors education, pharmacy programs, awareness have a powerful infuence on patient decision- campaigns and fnancial rewards, can impact making and behavioral change. Quick Fact The Health Belief Model proposes that patients act on treatment recommendations when they believe that the benefts of treatment outweigh treatment barriers. In a study of 18 small, medium and large pharmaceuticals companies, 12 had dedicated patient adherence teams. Human health behavior professionals, who can better understand patients’ motivations, psychology and emotions are increasingly a part of these teams. For example, the more the patient interest of preventing patients from switching to must change his or her lifestyle, the less likely he competitive offerings, infuencing positive health or she is to follow recommendations. In addition, outcomes and reducing the overall cost of health- the less complicated the treatment regimen, the care by offering a set of adherence services along higher the rate of adherence. The Emerging Adherence Paradigm Acquiring new patients costs pharmaceuticals of Patient Centricity companies an average of 62% more than retaining the ones they already serve. In addition, the less companies are now work- ing to engage with patients complicated the Approximately 69% of total healthcare costs are heavily infuenced by consumer behaviors.
Meta-analysis on the effectiveness of alcohol screening with brief interventions for patients in emergency care settings antibiotic resistant klebsiella best order opeazitro. Substance use screening bacteria under a microscope order cheapest opeazitro, brief intervention antibiotic quiz 100mg opeazitro amex, and referral to treatment for pediatricians. Screening for underage drinking and Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition alcohol use disorder in rural primary care practice. Motivational interviewing in medical care settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evidence-based treatment practices for substance use disorders: Workshop proceedings. Brief intervention for problem drug use in safety-net primary care settings: A randomized clinical trial. Screening, brief intervention, and referral for alcohol use in adolescents: A systematic review. Analysis of barriers to adoption of buprenorphine maintenance therapy by family physicians. Buprenorphine therapy for opioid addiction in rural Washington: The experience of the early adopters. Reducing fatal opioid overdose: Prevention, treatment and harm reduction strategies. A review of the efcacy and effectiveness of harm reduction strategies for alcohol, tobacco and illicit drugs. Assertive outreach: An effective strategy for engaging homeless persons with substance use disorders into treatment. The impact of syringe and needle exchange programs on drug use rates in the United States. Evidence for the effectiveness of sterile injecting equipment provision in preventing hepatitis C and human immunodefciency virus transmission among injecting drug users: A review of reviews. Preventing fatal overdoses: A systematic review of the effectiveness of take-home naloxone. Opioid overdose rates and implementation of overdose education and nasal naloxone distribution in Massachusetts: Interrupted time series analysis. Expanded access to naloxone: Options for critical response to the epidemic of opioid overdose mortality. Factors affecting detoxifcation readmission: Analysis of public sector data from three states. A performance measure for continuity of care after detoxifcation: Relationship with outcomes. Principles of adolescent substance use disorder treatment: A research-based guide. An improved diagnostic instrument for substance abuse patients: The Addiction Severity Index. The relative effectiveness of women-only and mixed-gender treatment for substance-abusing women. A randomized experimental study of gender-responsive substance abuse treatment for women in prison.
Purchase opeazitro cheap. Antimicrobial resistance.