
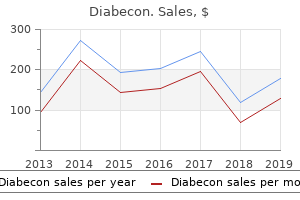
"Diabecon 60caps without a prescription, diabetic eye disease".
By: F. Alima, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Sanford School of Medicine of the University of South Dakota
Although the at early repair carried a high mortality rate and the two-stage anastomosis between the discontinuous and main pulmonary repair became universally favored diabetic myopathy cheap 60caps diabecon visa. In 1969 diabetes symptoms mood swings purchase diabecon 60 caps mastercard, Barratt-Boyes artery may require subsequent balloon angioplasty this is a and Neutze58 successfully reinitiated primary repair of symp- relatively simple diabetes test h1ac purchase diabecon 60caps visa, low risk procedure. In the 1970s, a systemic arterial shunt to the discontinuous pulmonary Castaneda et al. Venous cannulation is undertaken Taussig in 1945 with the establishment of the subclavian with thin-walled plastic right angle caval cannulas. Thick, rigid hypothermia (for example, 25–28°C) is employed to aid myo- dysplastic leafets that further narrow a small annulus area cardial protection and to reduce the infammatory effects of may require that a Z score closer to −2 than −3 triggers place- cardiopulmonary bypass. Depending on the chordal attach- patches, this approach has a disappointingly high need for ments of the tricuspid valve, as well as the proximity of the reoperation for recurrent obstruction. Location of the Ventriculotomy In particular, small and fragile premature babies (for During cooling, the anatomy of the coronary artery distri- example, <2 kg), it is usually preferable to employ elective bution needs to be carefully studied. Much of the initial phase of planned which will avoid division of the large right ventricu- the surgery can be undertaken on continuous cardiopulmo- lar coronary artery that extends toward the apex of the heart. The ventriculot- It is usually necessary to divide the branch of this artery omy, division of infundibular muscle and placement of initial which runs transversely at the narrowest area of muscular sutures can be undertaken on bypass. This will often require a slightly oblique incision in The ventricular approach using a limited infundibular inci- the infundibulum. This origin of the left pulmonary artery along the full length of approach offers several advantages over the atrial approach. If there is anything more resection of muscle which can lead to extensive endocardial than mild stenosis at the origin of the left pulmonary artery, scar formation. Several technical considerations need to be carefully observed if the Length of the Ventriculotomy ventricular approach is to be used correctly. It is important to limit the length of the ventriculotomy to the length of the infundibulum. Usually there is only a very small ligamentum is hypoplastic or absent, the incision can be limited to no arteriosum, but if there is a patent ductus arteriosus it should more than 5–6 mm. In all cases, the incision should fnish be ligated immediately after commencing bypass. The size several millimeters cephalad to the connection of the mod- of the main pulmonary artery and the diameter of the pul- erator band to the free wall of the right ventricle, which is monary annulus should be directly measured and compared also the origin of the anterior papillary muscle of the tricus- with the preoperative echo determinations. The incision should be extended across the annulus (transannular incision) when the Z score of the pulmonary annulus indicates that the annulus is smaller than 2–3 standard deviations below normal. These two muscle bundles usually fuse and aortic valves as is often the case, an alternative approach with the conal septum in patients with tetralogy and in a is to open the tricuspid valve and place sutures through from sense fx it in its abnormal anterior location. By dividing both the right atrial side of the septal leafets with the pledgets the parietal (free wall) and septal connections of the conal coming to lie in the right atrium. In practical terms, this means is also important to avoid taking large bites of folded tricus- that the surgeon carefully incises the left and right ends of pid valve leafet tissue as this will compromise subsequent the conal septum (Fig. Anchoring the sutures through the fbrous aortic annulus ensures that the sutures can be tied frmly and will It is particularly important to identify the moderator band not cut through the very soft muscular tissue of the young specifcally and to preserve this structure. It functions as a central pillar of the right ventricle and as such tethers the infant. Once the conal septum has been reached anteriorly, anterior free wall to the posterior septal wall. In older chil- there are no longer ridges and valleys as the conal septum dren, the moderator band may be quite hypertrophied and can is smooth and featureless up to the aortic valve. The Tefon pledgets are quite large surface associated with the septal band which should also be relative to the outfow area in a child who is less than 2 kg in divided in the older child.
Ayres Introduction The diagnosis of heart disease in utero has significantly evolved over the last 50 years blood glucose 233 diabecon 60caps on line, since the initial report of detecting a fetal heartbeat by ultrasonography in 1965 (1) metabolic disease dairy cows order diabecon online from canada. His contributions to the field were immense diabetes symptoms zinc-responsive dermatosis order diabecon 60caps online, starting with his first manuscript on fetal echocardiography published in 1980 (15). In this chapter we will review the implications of fetal diagnosis, fetal cardiac screening guidelines, indications for more detailed fetal echocardiography, and normal and abnormal fetal cardiovascular anatomy. Detailed discussion is included regarding the most common congenital heart lesions, fetal arrhythmias, and current research regarding fetal parental counseling. However, in population studies, the most recently reported rates of prenatal diagnosis of even major lesions are much lower and highly variable by practice and region, ranging from 20% to 42% (19,20,21,22,23). The significant variation is likely due to a combination of factors including limited access to prenatal care, technical limitations, experience of the sonographer or the medical care provider, time constraints, and patient- specific factors such as poor acoustic windows. Parental Preparation Fetal diagnosis of heart disease allows providers to better prepare and care for the family. One of the primary benefits for the family is the ability to learn about the condition and to decide where to seek treatment in a nonurgent manner compared to when the diagnosis is made postnatally. Families may discuss whether or not to continue the pregnancy, and this decision may be informed by additional testing including detailed extracardiac imaging and genetic studies (24). Parents not only have the opportunity for extensive counseling from both perinatology and pediatric cardiology, but also have the ability to meet with other specialists including cardiovascular surgeons, neonatologists, social workers, financial counselors, lactation specialists, nurses, and psychologists or psychiatrists if appropriate (25,26,27). Nonetheless, while prenatal diagnosis has many benefits for parental preparation, some studies suggest mothers with a prenatal diagnosis may have poorer bonding with the infant, possibly secondary to subconscious attempts to protect themselves emotionally in case of infant death (28). Morbidity and Mortality A prenatal diagnosis allows the medical team to optimize care for the neonate based on the anticipated hemodynamic status. This includes the choice of treatment center, planned delivery close to this facility, optimal early management to prevent hemodynamic deterioration, and prompt intervention if necessary (29,30,31,32,33). Measures of morbidity including oxygenation, myocardial function, blood pH, renal function, and perioperative neurologic events have been shown to be more optimal in prenatally diagnosed infants compared to those postnatally diagnosed (34,35,36,37,38,39,40). The question of whether prenatal diagnosis improves mortality has been elusive and controversial. Most published studies also have the significant limitation of care at a single tertiary care facility that does not account for death prior to transfer or prior to surgery. The authors showed more than a 6-fold greater preoperative mortality in neonates born more than 90 minutes from a cardiac surgical center, while postnatally diagnosed patients born close to a surgical center had preoperative mortality similar to those prenatally diagnosed. Fetal Cardiovascular Circulation Our understanding of human fetal circulation and changes attributable to cardiovascular disease was originally derived from early work with fetal lambs (50,51,52). Unlike the postnatal heart in which blood flow is in series, prenatally, the right and left fetal ventricular outputs run in parallel (Fig. This oxygenated blood accounts for approximately 50% of blood returning to the right atrium (Fig. Oxygenated blood enters the right atrium, and then is directed across the fetal foramen ovale to the left atrium by the Eustachian valve. Blood from the ascending aorta is then directed to the brain and upper extremities (73% of aortic output) while the rest is ejected to the inferior portion of the fetal body (27% of aortic output) and joins blood from the ductus arteriosus in the descending aorta. Reference ranges of blood flow in the major vessels of the normal human fetal circulation at term by phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging.

A positive preoperative response to oxygen diabetes definition by who buy diabecon 60caps mastercard, defined as a fall in the Rp/Rs of 30% diabetes insipidus quadro clinico purchase diabecon 60caps with amex, did not correlate with either operative survival or late Rp/Rs (213) diabetes type 2 prevention order 60 caps diabecon otc. Death occurred in 59 patients, with higher mortality rates in those operated on after the age of 2 5 years, those with pulmonary vascular resistance greater than 7 U × m , and those with complete heart block (Fig. Seventy-four of these underwent surgery and 12 died or developed right heart failure. Preoperative pulmonary vascular resistance, ratio of pulmonary blood flow to systemic blood flow, and ratio of pulmonary vascular resistance to systemic vascular resistance were 7. Thirty patients (79%) had a good outcome and were asymptomatic at a mean follow-up of 8. Eight patients (21%) had a poor outcome, but there was no significant difference regarding hemodynamic parameters at baseline between those who had a good outcome and those who did not (219). Those patients who are older and have desaturation or bidirectional shunting may benefit from vasodilator testing to stratify risk (221). Late results (30 to 35 years) after operative closure of isolated ventricular septal defect from 1954 to 1960. The algorithm is not applicable to complex conditions such as the absence of a subpulmonary ventricle (candidates to cavopulmonary anastomoses). In general, the term Eisenmenger syndrome is used mainly for shunts distal to the tricuspid valve, but some studies have included patients with a large atrial septal defect. The shunt is initially left to right, but as the underlying condition continues to increase P. Morbidity in Eisenmenger syndrome is common and includes: hemoptysis, pulmonary thromboembolism, stroke, and cerebral abscess. An increased risk of death has been shown related to noncardiac surgery with general anesthesia and maternal mortality. Current era survival of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with congenital heart disease: a comparison between clinical subgroups. Iron deficiency is common in patients with Eisenmenger syndrome and is associated with adverse events (243). Treatment of iron deficiency improves exercise capacity, but patients must be monitored for an increase in hemoglobin (244). Noncardiac operations on Eisenmenger patients are associated with a high mortality rate, and should be managed by a multidisciplinary team experienced in the care of patients with this condition. Nocturnal oxygen therapy in Eisenmenger syndrome does not appear to alter long-term outcome (245). Although patients with Eisenmenger syndrome are at risk for life- threatening thrombosis, anticoagulation is not associated with improved outcome (246). Compared with placebo, bosentan reduced pulmonary vascular resistance index and mean pulmonary arterial pressure and increased exercise capacity increased (53. In a separate study, in children treated with bosentan a progressive decline in exercise capacity was observed from 1-year follow-up, whereas in the adults, improvement lasted longer (251). Advanced therapies should be considered after other causes of functional limitation, such as iron deficiency, have first been addressed (252). Single Ventricle Circulation Pulmonary vascular resistance plays a key role in the outcome of the single ventricle patient. Although moderate altitude does not appear to alter outcome of the Fontan procedure in childhood (259), several studies suggest that travel to altitude or long- term residence at altitude may adversely affect long-term outcome of the Fontan procedure (260,261). B: Adjusted survival rate curves, based on the propensity score–adjusted Cox model, of patients within the third propensity score quartile, with and without advanced therapy. Improved survival among patients with Eisenmenger syndrome receiving advanced therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. In a randomized trial of 75 adolescents and adults with a Fontan circulation, bosentan improved exercise capacity, exercise time, and functional class without serious adverse events or hepatotoxicity (278).
Treatment with glucocorticoids is less effective diabete 500 glicemia buy cheap diabecon online; therefore diabetes insipidus renin purchase diabecon no prescription, antiandrogens and oral contra- ceptives are preferred for treatment of hirsutism and menstrual irregularities diabetes mellitus signs and symptoms pdf diabecon 60 caps with amex. However, glucocorticoids are in those with premature adrenarche and acceler- ated bone maturation. Prominent thecal hyperplasia and predominantly solid appearance of ova- ries with few or no cysts are characteristic of ovarian hyperthecosis on imaging. The case illustrated below shows severe virilization in a young girl with ovarian hyperthecosis. A detailed history and physical examination usually points to the diag- nosis of hyperandrogenic disorders. Patients who require workup include those with hirsutism (score >8-15 with menstrual irregularities or isolated hirsutism with score >15), menstrual irregularities, virilization, rapidly progressive hirsutism, infertility, galactorrhea, and stigma of Cushing’s syndrome. What are the minimum investigations required in a woman with disorder of androgen excess? Theca cells produce a regulated quantum of androgens which are available as a precursor for estradiol biosynthesis in granulosa cells. Therefore, the ovary becomes a major source of androgens and adipose tissue for estrogen. Endometrial estrogenization, timely ovulation, and progesterone withdrawal are the prerequisites for normal menstruation. Patients with oligomenorrhea with clinical estrogen sufficiency (Tanner breast stages 4–5) should be subjected to progesterone challenge (medroxyprogesterone acetate 10 mg/day for 5–7 days) after ruling out pregnancy. If progesterone withdrawal results in bleed- ing, it suggests that the endometrium is adequately primed with estrogen, and the cause of oligomenorrhea is anovulation. Absence of bleeding after with- drawal of progesterone suggests inadequate endometrial priming with estrogen. Patients with abnormalities in the hypothalamo–pituitary–ovarian axis like hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and hyperprolactinemia do not respond to progesterone withdrawal as they are estrogen deficient. Despite estrogen suf- ficiency, some women may not bleed with progesterone challenge and require further evaluation. In what situation a patient with secondary amenorrhea with estrogen defi- ciency may bleed on progesterone challenge test? In addition, patients on progesterone therapy may have progesterone breakthrough bleed despite estrogen insufficiency. Predictors of ovulation help in timing the ovulation and in deciding the fertility period. The markers of ovulation are regularity in menstrual cycles, increased basal body temperature (0. Treatment options depend on the need of patient and are listed in the table given below. Additive/ Primary concern Must First-line second line Hirsutism Lifestyle modification Oral contraceptive pills Antiandrogens Menstrual irregularities Lifestyle modification Oral contraceptive pills Metformin Metabolic abnormalities Lifestyle modification Metformin – (prediabetes/diabetes) Ovulation induction Lifestyle modification Clomiphene citrate Metformin 42. Patients with hirsutism and/or menstrual irregularities should be treated with oral contraceptives. In addition, some progestins have inhibitory effect on 5α-reductase activity and interfere with androgen action. Lone use of antiandrogens is con- traindicated as it may lead to menstrual irregularities (mid-cycle bleed due to deficient progesterone production/action) and can cause under-virilization in the male fetus, if conceived.
Purchase diabecon amex. Gâteau au chocolat sans sucre sans farine cétogène.