
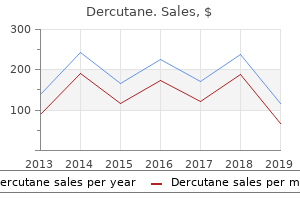
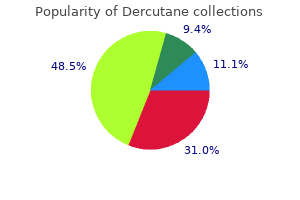
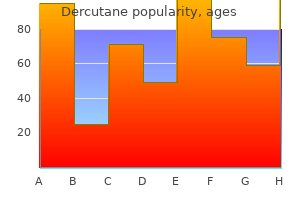
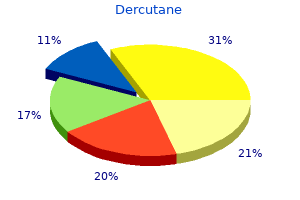
"Dercutane 40mg on line, acne while breastfeeding".
By: O. Lisk, M.A.S., M.D.
Vice Chair, Florida Atlantic University Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine
Bolus doses of propofol in the range of 1 to 2 mg per kg induce loss of consciousness within 30 seconds acne 9dpo buy 10 mg dercutane overnight delivery. Maintenance infusion rates of 100 to 200 μg/kg/min are adequate in younger subjects to maintain general anesthesia skin care routine for acne buy genuine dercutane on line, whereas doses should be reduced by 20% to 50% in elderly individuals acne studios sale generic dercutane 30mg. Propofol depresses ventricular systolic function and lowers afterload, but has no effect on diastolic function. In pigs, propofol caused a dose-related depression of sinus node and His-Purkinje system functions, but had no effect on atrioventricular node function or on the conduction properties of atrial and ventricular tissues. In patients with coronary artery disease, propofol administration may be associated with a reduction in coronary perfusion pressure and increased myocardial lactate production. Propofol decreases cerebral oxygen consumption, cerebral blood flow, and cerebral glucose utilization in humans and animals to the same degree as reported for thiopental and etomidate. Injection pain is less likely if the injection site is located proximally on the arm or if the injection is made via a central venous catheter. The emulsion used as the vehicle for propofol contains soybean oil and lecithin and supports bacterial growth; iatrogenic contamination leading to septic shock is possible. Accordingly, triglyceride levels should be monitored daily in this population whenever propofol is administered continuously for more than 24 hours. Not only does etomidate lack significant effects on myocardial contractility, but baseline sympathetic output and baroreflex regulation of sympathetic activity are well preserved. Etomidate depresses cerebral oxygen metabolism and blood flow in a dose-related manner without changing the intracranial volume–pressure relationship. Etomidate is particularly useful (rather than thiopental or propofol) in certain patient subsets: Hypovolemic patients, multiple trauma victims with closed head injury, and those with low ejection fraction, severe aortic stenosis, left main coronary artery disease, or severe cerebral vascular disease. Etomidate may be relatively contraindicated in patients with established or evolving septic shock because of its inhibition of cortisol synthesis (see below). Etomidate, when given by prolonged infusion, may increase mortality associated with low plasma cortisol levels [6]. Even single doses of etomidate can produce adrenal cortical suppression lasting 24 hours or more in normal patients undergoing elective surgery [7]. These effects are more pronounced as the dose is increased or if continuous infusions are used for sedation. Etomidate-induced adrenocortical suppression occurs because the drug blocks the 11β-hydroxylase that catalyzes the final step in the synthesis of cortisol. Since then, there have been several studies that have attempted to confirm or refute the safety of etomidate in critically ill patients, including those with sepsis. Unfortunately, some of these studies purportedly confirmed the danger of etomidate, whereas others support its continued use in patients with sepsis. Giving hydrocortisone to patients with septic shock may decrease overall mortality in patients who received etomidate for intubation as compared to other hypnotic agents [11]. Ketamine Description Ketamine induces a state of sedation, amnesia, and marked analgesia in which the patient experiences a strong feeling of dissociation from the environment. It is unique among the hypnotics in that it reliably induces unconsciousness by the intramuscular route. In the usual dosage, it decreases airway resistance, probably by blocking norepinephrine uptake that in turn stimulates beta-adrenergic receptors in the lungs. In contrast to many beta-agonist bronchodilators, ketamine is not arrhythmogenic when given to asthmatic patients receiving aminophylline.
The remainder of the fluid is sent for appropriate studies skin care on center discount dercutane online amex, which may include cytology; cell count and differential; protein; specific gravity; amylase; pH; lactate dehydrogenase; bilirubin; triglycerides; and albumin skin care jakarta timur purchase dercutane 30mg visa. Peritoneal fluid can be sent for smear and culture for acid-fast bacilli if tuberculous peritonitis is in the differential diagnosis acne 2007 discount dercutane 30mg otc. Catheter Technique Positioning; use of aseptic technique; and local anesthetic infiltration are the same as for the needle technique. This needle is removed from the peritoneal cavity and a catheter-over-needle assembly is used to gain access to the peritoneal cavity. If the anterior abdominal wall is thin, an 18- or 20-gauge Angiocath can be used as the catheter-over-needle assembly. If the anterior abdominal wall is quite thick, as in obese patients, it may be necessary to use a long (5. The catheter-over-needle assembly is inserted perpendicular to the anterior abdominal wall using the Z-track technique; once peritoneal fluid returns into the syringe barrel, the catheter is advanced over the needle, the needle is removed, and a 20- or 50-mL syringe is connected to the catheter. The tip of the catheter is now in the peritoneal cavity and can be left in place until the appropriate amount of peritoneal fluid is removed. When the Seldinger technique is used in patients with a large anterior abdominal wall, access to the peritoneal cavity is initially gained with a needle or catheter-over-needle assembly. A guidewire is then inserted through the needle and an 18- or 20-gauge single- or multiple-lumen central venous catheter is threaded over the guidewire. It is very important to use the Z-track method for the catheter technique to prevent development of an ascitic leak, which may be difficult to control and may predispose the patient to peritoneal infection. If continued drainage of a peritoneal fluid collection is desired, a radiologist or qualified proceduralist can place a chronic indwelling peritoneal catheter using a percutaneous guidewire technique. Complications the most common complications related to abdominal paracentesis are bleeding and persistent ascitic leak. Because most patients in whom ascites has developed also have some component of chronic liver disease with associated coagulopathy and thrombocytopenia, it is very important to consider correction of any underlying coagulopathy before proceeding with abdominal paracentesis. The Z-track technique is very helpful in minimizing persistent ascitic leak and should always be used. Another complication associated with abdominal paracentesis is intestinal or urinary bladder perforation, with associated peritonitis and infection. Intestinal injury is more common when the needle technique is used than when the catheter technique is used. Because the needle is free in the peritoneal cavity, iatrogenic intestinal perforation may occur if the patient moves or if intra-abdominal pressure increases with Valsalva maneuver or coughing. Urinary bladder injury is less common and underscores the importance of draining the urinary bladder with a catheter before the procedure. This injury is more common when the abdominal access site is in the suprapubic location; therefore, this access site is not recommended when direct visualization is not available. Percutaneous placement of a tunneled catheter is a viable and safe technique to consider in patients who have symptomatic malignant ascites that require frequent therapeutic paracentesis for relief of symptoms [23]. Abdominal paracentesis for the evaluation of hemoperitoneum was associated with a high false-negative rate. This clinical suspicion was confirmed by Giacobine and Siler [26] in an experimental animal model of hemoperitoneum documenting that a 500-mL blood volume in the peritoneal cavity yielded a positive paracentesis rate of only 78%. Many subsequent clinical studies confirmed these findings, with the largest series reported by Fischer et al. Diagnostic peritoneal aspiration, without a full lavage, has also been utilized successfully in these circumstances [32]. If the patient is hemodynamically unstable or requires emergent surgical intervention for a craniotomy, thoracotomy, or vascular procedure, it is imperative to determine whether there is a coexisting intraperitoneal source of hemorrhage to prioritize treatment of life-threatening injuries. A hemodynamically unstable patient with abdominal penetrating injuries requires no further investigation and immediate laparotomy should be undertaken.
The use of systemic antibiotics as prophylaxis before the placement of central venous devices is strongly discouraged because selection for antibiotic-resistant microorganisms is highly likely [3 acne research buy cheap dercutane 20mg on line,4] acne 5th grade cheap dercutane 30 mg online. Care of the Catheter and Insertion Site Insertion Site Dressings Either gauze and tape bandages or transparent semi-permeable dressings can be used for peripheral and central catheters skincare for over 60 purchase dercutane pills in toronto. Transparent dressings are changed every 5 to 7 days and gauze dressings every 2 days or more frequently if the dressing is soiled, loose, or damp [3]. Catheter Hub Disinfection Local disinfection of the hubs of central venous catheters must be performed using either a chlorhexidine-based preparation or 70% alcohol before attempting access [3,4]. With either preparation, it is very important to allow the antiseptic to dry to ensure antimicrobial activity before accessing the catheter. Maintenance of the catheter hub should be performed with strict standards, similar to those for insertion of catheters, to decrease the risk of contamination and infection [4]. A randomized controlled trial found that reducing the frequency of changing unsoiled adherent dressings from 3 to 7 days, and thus decreasing manipulation of the site, did not increase the risk of infection [36]. Catheter Replacement Peripheral Catheters Phlebitis of a peripheral vein is a well-recognized harbinger of infection and may be quite uncomfortable for the patient. Complications of peripheral venous catheter insertion, including phlebitis and catheter-associated infection, increase after 72 hours of insertion. Recommendations to remove and change these catheters to another site every 72 hours are aimed at decreasing the risk for infection and the discomfort associated with phlebitis [4]. Central Catheters the risk of infection increases during the time that a central catheter is in place, but several studies have shown that routine replacement of these catheters does not reduce rates of catheter-associated bloodstream infections [3,4]. Routine rotation of a central catheter to a different site is associated with increased risk for pneumothorax, laceration of a vessel with hemothorax, and arrhythmias and thus, is not recommended [5]. However, a meta- analysis of studies employing this technique failed to show an effect on decreasing infections, and routine catheter changes over a guidewire are not recommended [4,37]. An exception is made for the patient who has poor access and is dependent on a surgically implanted semipermanent central catheter. In-Line Devices and Filters In-line devices can be a significant source of catheter-associated infections. Pressure transducers have been implicated during outbreaks of catheter-associated bloodstream infection, particularly those due to water-associated gram-negative bacilli, including Pseudomonas, Serratia, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, and Acinetobacter spp. Stopcocks are easily contaminated through manipulation by personnel or by injection with contaminated syringes and may be an important source of infection; use of a closed system rather than stopcocks has been shown to lead to less contamination of the line. Some studies suggest that needleless mechanical valve devices may pose a greater risk of infection than split septum devices [40,41]. Disposable transducer domes, stopcocks, needleless components, and other in-line devices should be changed with the rest of the infusion set. All catheter hubs, needleless connectors, and injection ports should be disinfected with a chlorhexidine preparation before accessing the device [3]. Contamination of Infusates Breaks in sterile technique by hospital personnel can cause bloodstream infection. Gram-negative bacilli, such as Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Serratia, and Citrobacter, can proliferate in the acidic environment of intravenous fluids containing minimal nutrients, and other organisms, including fungi, can grow in parenteral nutrition infusates containing lipids [42,43]. Multifaceted Approach to Prevention of Catheter Infection An optimal approach to prevent catheter-associated infection involves the use of multiple infection control strategies, often termed a bundle. This bundle consisted of full-barrier precautions for catheter insertion; hand washing; insertion site cleansing with chlorhexidine; avoidance of femoral insertion site; and removal of unnecessary catheters. This was implemented in conjunction with clinician education, use of a designated central-line cart, a checklist to ensure adherence, and empowerment of the assistant to stop the procedure if the practices in the bundle were not being followed. This intervention led to a sustained 66% reduction in catheter-associated bloodstream infections over 18 months.
The remainder of cases are usually due to primary renal disorders acne 4 days before period dercutane 30 mg fast delivery, such as minimal change disease acne medicine buy cheap dercutane 20 mg, membranous nephropathy or focal segmen- tal glomerulosclerosis acne and diet discount 10 mg dercutane with mastercard. An alternative, therefore, is the urine protein–creatinine ratio performed on a random urine specimen. Patients with nephrotic syndrome should be referred to a nephrologist for further investigation and management. In adult patients, almost all will require a renal biopsy in order to reach a histological diag- nosis. For example, in minimal change disease, treatment is high-dose immunosupression in comparison to secondary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in which immunosu- pression exacerbates the disease. General measures aim to reduce proteinuria, peripheral oedema and hypercholester- olaemia and avoidance of complications. High doses of diuretic are often required as enteral absorption is often reduced due to gut mucosal oedema, as well as impaired drug delivery to the kidney as a consequence of hypoalbuminaemia. In order to avoid renal impairment asso- ciated with these drugs, regular monitoring of kidney function is advocated. The aim should be to achieve 1 kg weight loss per day in order to avoid hypovolaemia/ hypotension and subsequent kidney injury, while maintaining adequate diuresis. Hyperlipidaemia is treated in the conventional way with careful dietary modifica- tion and the addition of statins or other lipid-lowering drugs. The nephrotic syndrome is associated with a hypercoagulable state due to loss of fibrinolytic factors in the urine and increased hepatic synthesis of clotting factors. There is subsequently an increased incidence of arterial and venous thrombosis (in particular renal vein and deep vein thrombosis). Clinicians should hold a low index of suspicion for the development of any thrombotic condition and early investigation and treatment are imperative. Pneumococcal infection is particularly common, therefore patients should be offered pneumococcal vaccina- tion. Acute kidney injury may occur due to several factors, including overzealous diuresis, hypovolaemia, as well as a complication of the underlying renal disease. She was found in the bath at home with evidence of cuts to her wrists and with three empty boxes of paracetamol on the floor. On further questioning, she had had an argument with her partner that evening, who found her and called the ambulance. Further details from her partner revealed that she was known to the mental health services with a recent diagnosis of depression. Examination Examination reveals a tearful woman who is difficult to engage and not maintain- ing eye contact. Paracetamol is metabo- lized by the liver and is conjugated with glutathione and subsequently excreted as cysteine and mercapturic conjugates. In overdose, the large amounts of paracetamol exceed the capability of the glutathione conjugation pathway. Consider activated charcoal if presentation is within 1 hour to bind the paracetamol and hence prevent its absorption by the gastrointestinal tract. The risk of severe liver damage is assessed according to the paracetamol concentration/time from ingestion graph (ure 94. The high-risk treatment line should be used if there is history of malnourish- ment/alcoholism/pre-existing liver disease/chronic debilitating illness (e.
However acne 40s discount dercutane 30mg with mastercard, estrogen accelerates the conjuga- tion of metyrapone by the liver; and acne redness safe 30mg dercutane, therefore acne laser treatment cost purchase dercutane australia, the drug has less efect, thus explaining the subnormal responses initially reported. Prior to the introduction of methods for measuring free thyroxine levels, evaluation of thyroid function was a problem. Oral contraception afects the total thyroxine level in the blood as well as the amount of binding globulin, but the free thyroxine level is unchanged. Early studies that indicated adverse efects have not stood the test of time and the scrutiny of multiple, careful studies. Tere are two major areas that warrant review: (1) Inadvertent use of oral contraceptives during the cycle of conception and during early pregnancy, and (2) repro- duction afer discontinuing oral contraception. Inadvertent Use During the Cycle of Conception and During Early Pregnancy One of the reasons, if not the major reason, why a lack of withdrawal bleed- ing while using oral contraceptives is such a problem is the anxiety produced in both patient and clinician. The patient is anxious because of the uncer- tainty regarding pregnancy, and the clinician is anxious because of the con- cerns stemming from the retrospective studies that indicated an increased risk of congenital malformations among the ofspring of women who were pregnant and using oral contraception. Organogenesis does not occur in the frst 2 embryonic weeks (frst 4 weeks since last menstrual period); however, teratogenic efects are possible between the third and the eighth embryonic weeks (5 to 10 weeks since last menstrual period). Initial positive reports linking the use of contraceptive steroids to con- genital malformations have not been substantiated. Many suspect a strong component of recall bias in the few positive studies due to a tendency of patients with malformed infants to recall details better than those with nor- mal children. Other confounding problems have included a failure to con- sider the reasons for the administration of hormones (e. Col- laborative Perinatal Project; however, subsequent analysis of these data uncovered several methodologic shortcomings. This recommendation can be extended to those pregnant woman who have been exposed to a progestational agent such as medroxyprogesterone acetate or 17-hydroxyprogesterone caproate. In the Oxford Family Planning Association study, former use had an efect on fer- tility for up to 42 months in nulligravida women and for up to 30 months in multigravida women. A later analysis of the Oxford data indicated that the delay was concen- trated in women aged 30 to 34 who had never given birth. Childless women age 25 to 29 experienced some delay in return to fertility, but by 48 months, 91% had given birth compared with 92% in users of other methods. In the Boston area, the interval from cessation of contraception to conception was 13 months or greater for 24. Similar fndings in Connecticut indicated that this delay lasted at least a year, and the efect was greater with higher dose preparations. In fact, in young women, previous oral contraceptive use is associated with a lower risk of primary infertility. In a prospective study from the United Kingdom refecting mod- ern, low-dose oral contraceptives, no delay to conception was found and A Clinical Guide for Contraception long-term use was actually associated with greater fertility. The early and 1-year pregnancy rates afer discontinuation of oral contraceptives were not negatively afected, regard- less of progestin type, duration of use, or parity. The previous reports indicating a delay in achieving pregnancy may have been infuenced not only by higher dose products, but also by a failure to account for declining fertility with aging and the prescribing of oral contraceptives to women with anovulatory, irregular menstrual periods. It is unlikely that women discontinuing low-dose steroid contraception experience any sig- nifcant delay in achieving pregnancy compared with the experience in a general population. Spontaneous Miscarriage Tere is no increase in the incidence of spontaneous miscarriage in pregnan- cies afer the cessation of oral contraception. Indeed, the rate of spontaneous miscarriages and stillbirths is slightly less in former pill users, about 1% less for spontaneous miscarriages and 0.
Discount dercutane 30 mg amex. WHERE I BUY K-BEAUTY 🛍️ MY FAV SHOPS.