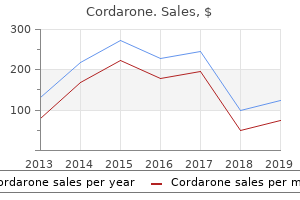

"Cheap cordarone uk, medications given to newborns".
By: L. Renwik, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of Nevada, Las Vegas School of Medicine
Activ- the activity front reaches the recording point keratin treatment cheap generic cordarone canada, the propul- ity in the stomach appears to migrate into the duodenum sive segment of every peristaltic wave is detected medicine cabinets surface mount 100mg cordarone. The time during which 0 components of solid and liquid meals 0 0 0 enter and leave the stomach 88 treatment essence generic cordarone 200 mg, duodenum, Time after ingestion of meal (hr) and large intestine is measured in hours. CHAPTER 26 Neurogastroenterology and Gastrointestinal Motility 473 Pressure recording port on catheter MMC activity front 0 5 10 15 20 25 Time (min) FIGURE 26. This time is shortest in the It continues in the small intestine after a vagotomy or sym- duodenum and progressively increases as the MMC mi- pathectomy but stops when it reaches a region of the intes- grates toward the ileum. Presumably, The MMC is seen in most mammals, including humans, command signals to the enteric neural circuits are necessary in conscious states and during sleep. It starts in the antrum for initiating the MMC, but whether the commands are of the stomach as an increase in the strength of the regu- neural, hormonal, or both is unknown. Although levels of larly occurring antral contractile complexes and accom- the hormone motilin increase in the blood at the onset of plishes the emptying of indigestible particles (e. In humans, 80 to 120 minutes released as a consequence of its occurrence. As one activity front termi- nates in the ileum, another begins in the antrum. Gallbladder contrac- mans, the time between cycles is longer during the day than tion and delivery of bile to the duodenum is coordinated at night. The activity front travels at about 3 to 6 cm/min in with the onset of the MMC in the intraduodenal region. It is important not to confuse the MMC propels the bile to the terminal ileum, where it is re- speed of travel of the activity front of the MMC with that absorbed into the hepatic portal circulation. This mecha- of the electrical slow waves, action potentials, and peri- nism minimizes the accumulation of concentrated bile in staltic waves within the activity front. Slow waves with as- the gallbladder and increases the movement of bile acids in sociated action potentials and associated contractions of the enterohepatic circulation during the interdigestive state circular muscle travel about 10 times faster. Cycling of the MMC continues until it is ended by the The adaptive significance of the MMC appears also to ingestion of food. A sufficient nutrient load terminates the be a mechanism for clearing indigestible debris from the in- MMC simultaneously at all levels of the intestine. Large indigestible nation requires the physical presence of a meal in the upper particles are emptied from the stomach only during the in- digestive tract; intravenous feeding does not end the fasting terdigestive state. The speed with which the MMC is terminated at Bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine is associated all levels of the intestine suggests a neural or hormonal with an absence of the MMC. Gastrin and cholecystokinin, both of which the MMC may play a housekeeper role in preventing the are released during a meal, terminate the MMC in the overgrowth of microorganisms that might occur in the stomach and upper small intestine but not in the ileum, small intestine if the contents were allowed to stagnate in when injected intravenously. When the vagus nerves are blocked during the digestive state, MMCs A mixing pattern of motility replaces the MMC when the reappear in the intestine but not in the stomach. With small intestine is in the digestive state following ingestion warming of the nerves and release of the neural blockade, of a meal. The mixing movements are sometimes called the mixing motility pattern returns. Peri- staltic contractions, which propagate for only short dis- tances, account for the segmentation appearance.
Use a simple diagram to show the parasympathetic inner- provide parasympathetic innervation to the lower half of the large vation of the heart treatment toenail fungus purchase cordarone with paypal. Label the preganglionic and postgan- intestine medicine mound texas order generic cordarone line, the rectum medicine dictionary 100 mg cordarone for sale, and to the urinary and reproductive systems. Describe the distribution of the vagus nerve and discuss the the visceral organs thus consist of preganglionic neurons, whereas functional significance of this distribution. Define the terms white rami and gray rami and explain why A composite view of the sympathetic and parasympathetic blood vessels in the skin and skeletal muscles receive sym- divisions of the ANS is provided in figure 13. Describe the structure of the adrenal gland and explain its relationship to the sympathetic division of the ANS. Autonomic Nervous © The McGraw−Hill Anatomy, Sixth Edition Coordination System Companies, 2001 444 Unit 5 Integration and Coordination TABLE 13. The actions of the autonomic nervous system, together with the effects of hormones, help to maintain a state of dynamic con- Neurotransmitters of the Autonomic stancy in the internal environment. The sympathetic division gears the body for action through adrenergic effects; the parasympa- Nervous System thetic division conserves the body’s energy through cholinergic ef- The neurotransmitter released by most postganglionic sympa- fects. Homeostasis thus depends, in large part, on the thetic neurons is norepinephrine (noradrenaline). There are a few exceptions to this rule: some sympathetic neu- Objective 8 List the neurotransmitters of the preganglionic rons that innervate blood vessels in skeletal muscles, as well as and postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic and sympathetic neurons to sweat glands, release acetylcholine (are parasympathetic divisions. Acetylcholine is also the transmitter released by all Objective 10 Explain the antagonistic, complementary, and parasympathetic postganglionic neurons at their synapses with cooperative effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic effector cells (fig. In other words, a cholinergic fiber is a neuron that secretes ACh at the terminal end of its axon. Mass acti- vation of the sympathetic division prepares the body for intense Responses to Adrenergic Stimulation physical activity in emergencies; the heart rate increases, blood glucose rises, and blood is diverted to the skeletal muscles (away Adrenergic stimulation—by epinephrine in the blood and by nor- from the visceral organs and skin). These and other effects are epinephrine released from sympathetic nerve endings—has both listed in table 13. The theme of the sympathetic division is excitatory and inhibitory effects. The heart, dilatory muscles of aptly summarized in the phrase fight or flight. The smooth muscles of the bronchioles and of many ways opposite to the effects of sympathetic stimulation. The some blood vessels, however, are inhibited from contracting; parasympathetic division, however, is not normally activated as a adrenergic chemicals, therefore, cause these structures to dilate. Stimulation of separate parasympathetic nerves can result in slowing of the heart, dilation of visceral blood vessels, and in- creased activity of the GI tract (table 13. Autonomic Nervous © The McGraw−Hill Anatomy, Sixth Edition Coordination System Companies, 2001 Chapter 13 Autonomic Nervous System 445 TABLE 13. This drug, however, does not affect the cholinergic receptors of skele- Somatic motor neurons, postganglionic parasympathetic neu- tal muscle or those of autonomic ganglia. The acetylcholine re- rons, and all preganglionic autonomic neurons are cholinergic— ceptors of visceral organs are therefore said to be muscarinic. The cholinergic effects of somatic motor neurons and preganglionic autonomic The muscarinic effects of ACh are specifically inhibited by the drug atropine, derived from the deadly nightshade plant neurons are always excitatory. Indeed, extracts of this plant were used glionic parasympathetic neurons are usually excitatory, with by women during the Middle Ages to dilate their pupils (at- some notable exceptions; the parasympathetic neurons innervat- ropine inhibits parasympathetic stimulation of the iris). Autonomic Nervous © The McGraw−Hill Anatomy, Sixth Edition Coordination System Companies, 2001 446 Unit 5 Integration and Coordination Central Nervous System Cranial Terminal parasympathetic ganglion nerves Visceral ⊃• ACh ACh effectors Paravertebral ganglion ⊃• NE Visceral ACh effectors Adrenal medulla Sympathetic ACh E, NE (hormones) (thoracolumbar) nerves ⊃ • NE Visceral ACh effectors Collateral ganglion Sacral parasympathetic Visceral nerves ⊃ • effector ACh ACh organs FIGURE 13. Those nerves that release ACh are called cholinergic; those that release NE are called adrenergic.
There were fewer claims for older women symptoms sleep apnea purchase cordarone paypal, but 10 of 17 (59%) paid indemnity treatment 24 seven order generic cordarone pills. BREAST BIOPSY AND THE MICROSCOPIC DIAGNOSIS OF BREAST CANCER We turn now to an analysis of the clinical and medical-legal issues surrounding the microscopic diagnosis of breast cancer symptoms torn rotator cuff order 100mg cordarone fast delivery. In a separate study of pathology claims, TDC reviewed 218 con- secutive surgical pathology and fine needle aspiration (FNA) claims from 1995 to 1997 (7–9). Breast FNA accounted for 6% of these claims and breast biopsy accounted for another 14%. When claims involving breast FNA, breast biopsy, and breast frozen section were combined, breast specimens accounted for 22% of all pathology claims. Fifty- four percent of breast biopsy claims involved the false-negative diag- nosis of breast carcinoma, whereas 35% were for the false-positive diagnosis of carcinoma. Breast Fine Needle Aspiration A false-negative breast FNA usually results from the failure to adequately sample a breast mass (sampling error) and is responsible for the majority of claims. Often, these claims involve a woman with a palpable breast mass, in whom an FNA is negative, and who is subsequently diagnosed with carcinoma. In many of these cases, an FNA diagnosis of “fibrocystic change” or “negative” was made on sparsely cellular smears. Although the definition of breast FNA speci- men adequacy is controversial (10–12), it is important to remember that many physicians perform FNA procedures infrequently and lack formal training in smear preparation technique. For this reason, they are often unable to reliably assess whether or not the mass was adequately sampled. Therefore, when the slides have only a few cells, Chapter 12 / Breast Cancer Litigation 161 it is hazardous for a pathologist to assume that the specimen is a rep- resentative sample and proceed to make a diagnosis of fibrocystic change or negative. This is a special problem in a managed care envi- ronment where patients frequently change health plans—and physi- cians—and are often lost to follow-up. Most of these claims could have been prevented if the diagnosis had been “nondiagnostic because of sparse cellularity, additional diagnostic studies recommended. Triple Test Strategy Every breast FNA report should include a statement reminding the clinician that breast FNA has a false-negative rate of 3–5% and a false- positive rate of 0. The consequences of these errors can be mini- mized by applying the triple test strategy, that is, correlating the FNA results with the mammogram/ultrasound findings and the clinical breast examination and performing a biopsy if these are discordant. Whenever possible, the pathologist should review the mammogram and ultrasound reports and discuss the physical findings with the cli- nician before releasing the FNA report. If the pathologist knows there is triple test discordance, then this should be stated in the report and biopsy recommended. This strategy would eliminate most liability claims for breast FNA and result in improved clinical outcomes. Claims resulting from false-positive FNAs usually are caused by interpretation errors. Most commonly, an FNA diagnosis of carcinoma is made on a mass subsequently shown to be a fibroadenoma. The claim results from either unnecessary mastectomy or axillary node sampling if breast conservation is elected. In almost every instance, these claims would have been prevented if the triple test strategy had been applied. Breast Biopsy Some breast biopsy claims involve the differentiation of low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) from ductal involvement by lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS). It is hoped that the use of immunostains for E-cadherin will add objectivity to this distinction (13,14).
This movement is sensed by displacement of the stereocilia of the hair cells treatment junctional tachycardia order cordarone 100mg with mastercard. These cells are much like those of the organ of Corti symptoms 10 days post ovulation 200 mg cordarone with amex, except that at the “tall” end of the stereocilia array there is one larger cilium medications similar to vyvanse generic cordarone 100mg with visa, the kinocilium. When the stereocilia are bent toward the kinocilium, the frequency of action potentials in the afferent neurons leaving the am- pulla increases; bending in the other direction decreases the action potential frequency. The role of the semicircular canals in sensing rotary ac- celeration is shown on the left side of Figure 4. The mechanisms linking stereocilia deflection to receptor po- The vestibular apparatus in the bony tentials and action potential generation are quite similar to FIGURE 4. Because of the inertia of the canals sense rotary acceleration and motion, while the utricle and endolymph in the canals, when the position of the head is saccule sense linear acceleration and static position. The vestibular apparatus is an important component in several reflexes that serve to orient the body in space and maintain that orientation. Integrated responses to Slow eye Head rotation movements Slow movement FIGURE 4. A, The crista ampularis contains the hair (receptor) cells, and the whole structure is deflected by mo- tion of the endolymph. The fluid cur- rents are roughly proportional to the rate of change of ve- Slow locity (i. As a re- sult of the bilateral symmetry in the vestibular system, canals FIGURE 4. This sensation is vestibular division of cranial nerve VIII passes the impulses linked to compensatory eye movements by the vestibuloocular re- first to the vestibular ganglion, where the cell bodies of the flex. The information is then passed canals is shown as if one were looking down through the top of a to the vestibular nuclei of the brainstem and from there to head looking toward the top of the page. Within the ampulla of various locations involved in sensing, correcting, and com- each canal is the cupula, an extension of the crista ampullaris, the pensating for changes in the motions of the body. The remaining vestibular organs, the saccule and the utri- Below each canal is the action potential train recorded from the cle, are also part of the membranous labyrinth. A, The head is still, and equal nerve activity is municate with the semicircular canals, the cochlear duct, seen on both sides. The sensory structures in these of the endolymph causes it to lag behind the movement, produc- organs, called maculae, also employ hair cells, similar to ing a fluid current that stimulates the cupulae (arrows show the those of the ampullar cristae (Fig. Because the two canals are cells are covered with the otolithic membrane, a gelatinous mirror images, the neural effects are opposite on each side (the substance in which are embedded numerous small crystals of cupulae are bent in relatively opposite directions). Because the tion causes the eyes to move slowly to the right, opposite to the otoliths are heavier than the endolymph, tilting of the head direction of rotation (right column); they then snap back and be- results in gravitational movement of the otolithic membrane gin the slow movement again as rotation continues. The fast and a corresponding change in sensory neuron action po- movement is called rotatory nystagmus. As in the ampulla, the action potential fre- the endolymph “catches up” with the canal because of fluid fric- tion and viscosity, and there is no relative movement to deflect quency increases or decreases depending on the direction of the cupulae. D, When the rotation stops, the inertia of signal in response to displacement; in addition, they are lo- the endolymph causes a current in the same direction as the pre- cated away from the semicircular canals and are not subject ceding rotation, and the cupulae are again deflected, this time in a to motion-induced currents in the endolymph. The slow eye move- them to monitor the position of the head with respect to a ments now occur in the same direction as the former rotation. The Special Chemical Senses Detect Molecules in the Environment Chemical sensation includes not only the special chemical senses described below, but also internal sensory receptor functions that monitor the concentrations of gases and other chemical substances dissolved in the blood or other body fluids. Since we are seldom aware of these internal chemical sensations, they are treated throughout this book as needed; the discussion here covers only taste and smell. The sense of taste is mediated by multicellular receptors called taste buds, several thousand FIGURE 4. The gravity-driven movement of the otoliths stimulates the the tops of the numerous fungiform papillae but are also lo- hair cells.
Order cordarone cheap online. Depression Symptoms: Signs of Depression.