

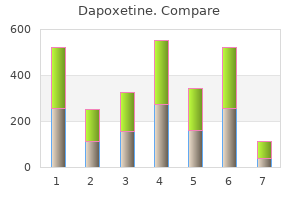
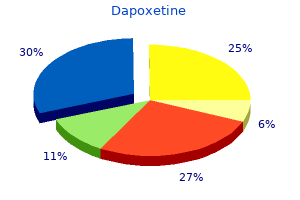
"Cheap dapoxetine 90mg, impotence specialist".
By: D. Ingvar, MD
Co-Director, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine
If arrhythmia does supportive measures while they metabolise and eliminate lead to persistent peripheral circulatory failure impotence juicing purchase dapoxetine online pills, an the poison erectile dysfunction yahoo buy discount dapoxetine. A few will require a b-adrenoceptor blocker for poisoning with a administration of a specific antidote erectile dysfunction essential oils purchase 30 mg dapoxetine mastercard. Aggressive volume Most patients recover from acute poisonings repletion and correction of acid–base abnormality are provided they are adequately oxygenated, hydrated needed; urine alkalinisation and/or diuretic therapy and perfused. From the environment Unless a patient has an intact or protected airway its admin- When a poison has been inhaled or absorbed through the istration is contraindicated. Volunteer studies suggest that administration within 1 h can be expected to prevent up to 40–50% of absorption. From the alimentary tract 1 There are no satisfactorily designed clinical trials in (‘gut decontamination’) patients to assess the benefit of single dose activated char- Gastric lavage should not be employed routinely, if ever, in coal. The procedure may be mechanical bowel obstruction may follow repeated considered in very extraordinary circumstances for the hos- use. In the drowsy or comatose patient there is particular pitalised adult who is believed to have ingested a poten- risk of aspiration into the lungs causing hypoxia through tially life-threatening amount of a poison within the obstruction and arteriovenous shunting. Methionine, previous hour, and provided the airways are protected by used orally for paracetamol poisoning, is adsorbed by a cuffed endotracheal tube. Fuller’s earth and where there is risk of haemorrhage from an underlying (a natural form of aluminium silicate) binds and inacti- gastrointestinal condition. Activated charcoal (Carbomix) consists of a very fine black powder prepared from vegetable matter, in the management of the poisoned patient. This binds to , and thus in- 2Forcenturiesitwassupposednotonlythattherecouldbe,butthatthere activates, a wide variety of compounds in the gut. This was Theriaca Andromachi, a formulation of 72 (a magical number) ingredients among which particular importance was attached to the flesh of a 1Joint position statements and guidelines agreed by the American snake (viper). Poison Centres and Clinical Toxicologists review the therapeutic 3Irrigation with large volumes of a polyethylene glycol–electrolyte usefulness of various procedures for gut decontamination. Klean-Prep, by mouth causes minimal fluid and appear in the Journal of Toxicology, Clinical Toxicology from 1997 electrolyte disturbance (it was developed for preparation for onwards, the latest position statements being in 2004 and 2005. In adults, activated charcoal 50 g the removal of sustained-release or enteric-coated formula- is given initially, then 50 g every 4 h. Vomiting should be tions from patients who present more than 2 h after inges- treated with an antiemetic drug because it reduces the tion, e. Activated charcoal in frequent (50 g) doses is the dose may be reduced and the frequency increased, generally preferred. Whole-bowel irrigation is also an option for the removal Alteration of urine pH and diuresis of ingested packets of illicit drugs. It is contraindicated in patients with bowel obstruction, perforation or ileus, It is useful to alter the pH of the glomerular filtrate such that with haemodynamic instability and with compromised a drug that is a weak electrolyte will ionise, become less unprotected airways. The effectiveness of activated this process, but the alteration of tubular fluid pH is the im- charcoal may be reduced by co-administration with whole portant determinant. Alkalinisation4 may be used for: salicylate (>500 mg/ Techniques for eliminating absorbed poisons have a role Lþmetabolic acidosis, or in any case >750 mg/L) pheno- that is limited, but important when applicable. Repeated doses of activated Haemodialysis charcoal The system requires a temporary extracorporeal circulation, Activated charcoal by mouth not only adsorbs ingested e.
The oral bioavailability of all three quinidine-based drugs is moderate and generally equals 70% reflecting first-pass metabolism in the intestinal wall and liver erectile dysfunction treatment in tampa discount 60 mg dapoxetine overnight delivery. The recommended dose of quinidine is based on the concurrent disease states and con- ditions present in the patient that can influence quinidine pharmacokinetics erectile dysfunction yoga exercises discount dapoxetine generic. Quinidine pharmacokinetic parameters used to compute doses are given in the following section for specific patient profiles erectile dysfunction treatment natural medicine cheap dapoxetine generic. Patients with liver cirrhosis have increased quinidine clearance and volume of distribution which results in a prolonged average quinidine half-life of 9 hours. Volume of distribution is larger due to decreased α1- acid glycoprotein and albumin production by liver which decreases drug binding in the plasma. Cardiac status must be monitored closely in heart failure patients since quinidine clearance changes with acute changes in cardiac output. Decreased plasma protein binding also leads to higher unbound levels for a given total quinidine serum concentration. For example, a quinidine total serum concentration of 3 μg/mL would yield an unbound concentration of 0. The significance of this difference in unbound con- centrations has not been assessed in cirrhosis patients, but clinicians should bear it in mind when monitoring quinidine levels as only total serum concentrations are available from laboratories. The exact effect that liver disease has on quinidine pharmacokinetics is highly variable and difficult to accurately predict. It is possible for a patient with liver disease to have relatively normal or grossly abnormal quinidine clearance, volume of dis- tribution, and half-life. An index of liver dysfunction can be gained by applying the Child-Pugh clinical classification system to the patient (Table 9-2). The Child-Pugh score consists of five laboratory tests or clinical symptoms: serum albumin, total biliru- bin, prothrombin time, ascites, and hepatic encephalopathy. Each of these areas is given a score of 1 (normal) to 3 (severely abnormal; Table 9-2), and the scores for the five areas are summed. The Child-Pugh score for a patient with normal liver function is 5 while the score for a patient with grossly abnormal serum albumin, total bilirubin, and prothrombin time values in addition to severe ascites and hepatic encephalopathy is 15. A Child-Pugh score greater than 8 is grounds for a decrease of 25–50% in the initial daily drug dose for quinidine. As in any patient with or without liver dysfunction, initial doses are meant as starting points for dosage titration based on patient response and avoidance of adverse effects. Quinidine serum concentrations and the presence of adverse drug effects should be monitored frequently in patients with liver cirrhosis. Because both clearance and volume of distribution simultaneously decrease, patients with heart failure have an average quinidine half-life equal to 7 hours which is similar to a normal individual [t1/2 = (0. Increased plasma pro- tein binding also leads to lower unbound levels for a given total quinidine serum concen- tration. For example, a quinidine total serum concentration of 3 μg/mL would yield an unbound concentration of 0. The clinical significance of this difference in unbound concentrations has not been assessed in heart failure patients. It is possible for a patient with heart failure to have relatively nor- mal or grossly abnormal quinidine clearance and half-life. For heart failure patients, ini- tial doses are meant as starting points for dosage titration based on patient response and avoidance of adverse effects. Quinidine serum concentrations and the presence of adverse drug effects should be monitored frequently in patients with heart failure. Patients with myocardial infarction may develop serious arrhythmias that require ther- apy with quinidine. Because quinidine is considered a moderate hepatic extraction ratio drug, a decline in the unbound fraction of quinidine in the plasma decreases quinidine clearance.
Order 60mg dapoxetine overnight delivery. With Erectile Dysfunction There are Many Options for Treatment.
If the dosage is adjusted impotence kit cheap 90mg dapoxetine mastercard, vancomycin elimination changes or laboratory and clinical monitoring indicate that the infection is not resolving or worsening erectile dysfunction treatment natural in india 30mg dapoxetine otc, clinicians should consider rechecking steady-state drug concentrations erectile dysfunction drug therapy discount dapoxetine generic. While some clinicians continue to monitor both steady-state peak and trough vancomycin serum concentrations, most individuals advocate the measurement of just a steady-state trough concentration. Since nephrotoxicity is related to high trough concentrations, measurement of this value should ensure therapeutic, nonnephrotoxic drug concentrations. Based on this, the argument has been made that if a patient has a ther- apeutic steady-state trough concentration (5–15 μg/mL) and the dose is in the usual range (500–1500 mg), it is difficult to produce a steady-state peak concentration that would be above the accepted toxic range (>80 μg/mL). If a patient developed ototoxicity while receiving vancomycin, it could be difficult to prove that steady-state peak concentrations were in the acceptable range if no serum concentrations were obtained at that time. Clinicians should consider measuring peak concentrations when large doses are given (>1500 mg/dose) or for infections that require high peak concentrations (such as central nervous system infections). Ideally, a baseline serum creatinine concentration is obtained before vancomycin therapy is initiated and three times weekly during treatment. An increasing serum creati- nine test on two or more consecutive measurement occasions indicates that more inten- sive monitoring of serum creatinine values, such as daily, is needed. Instead, clinical signs and symptoms of auditory (decreased hearing acuity in the conver- sational range, feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears, tinnitus) or vestibular (loss of equilibrium, headache, nausea, vomiting, vertigo, nystagmus, ataxia) ototoxicity are monitored at the same time intervals as serum creatinine determination. When high vancomycin concentrations are needed for therapeutic reasons (trough >15 μg/mL, peak >40 μg/mL), assessment of renal function and auditory/vestibular function should be con- ducted on a daily basis. Vancomycin can also cause allergic symptoms such as chills, fever, skin rashes, and anaphylactoid reactions. Intramuscular administration is usually avoided because this route has been reported to cause tissue necrosis at the site of injection. Oral bioavail- ability is poor (<10%) so systemic infections cannot be treated by this route of adminis- tration. Since vancomycin is eliminated principally by glomerular filtration, renal dysfunction is the most important disease state that influences vancomycin pharmacokinetics. Major body burns (>30–40% body surface area) can cause large changes in van- comycin pharmacokinetics. The increase in basal metabolic rate causes an increase in glomerular filtration rate which increases van- comycin clearance. Because of the increase in drug clearance, the average half-life for vancomycin in burn patients is 4 hours. Obese individuals with normal serum creatinine concentrations have increased van- comycin clearance secondary to increased glomerular filtration rate and are best dosed with vancomycin using total body weight. While the average dose in morbidly obese and normal weight patients with normal serum creatinine concentrations was ~30 mg/kg/d using total body weight in both populations, some morbidly obese patients required every-8-hour dosing to maintain vancomycin steady-state trough con- centrations above 5 μg/mL. Full-term neonates (gesta- tional age ~40 weeks) have similar volumes of distribution for vancomycin compared to premature infants, but their vancomycin clearance rate is twice that found in infants born prematurely (30 mL/min). At about 3 months of age, vancomycin clearance has nearly doubled again (50 mL/min) resulting in a half-life of approximately 4 hours. The increase in vancomycin clearance continues through 4–8 years of age when clearance equals 130–160 mL/min while vol- ume of distribution remains ~0. At that time, van- comycin clearance and half-life gradually approach adult values as puberty approaches in children (~12–14 years old). The effect that hemodialysis has on vancomycin pharmacokinetics depends upon the type of artificial kidney used during the procedure.
A parallel system for angiotensin generation exists in several other tissues (eg erectile dysfunction age onset best order dapoxetine, heart) and may be responsible for trophic changes such as cardiac hypertrophy erectile dysfunction can cause pregnancy buy dapoxetine online. A fourth group of drugs erectile dysfunction treatment perth discount dapoxetine online american express, the aldosterone receptor inhibitors (eg, spironolactone, eplerenone) are discussed with the diuretics. The hypotensive activity of captopril results both from an inhibitory action on the renin-angiotensin system and a stimulating action on the kallikrein-kinin system (Figure 11–5). The latter mechanism has been demonstrated by showing that a bradykinin receptor antagonist, icatibant (see Chapter 17), blunts the blood pressure-lowering effect of captopril. Enalapril is an oral prodrug that is converted by hydrolysis to a converting enzyme inhibitor, enalaprilat, with effects similar to those of captopril. Benazepril, fosinopril, moexipril, perindopril, quinapril, ramipril, and trandolapril are other long-acting members of the class. All are prodrugs, like enalapril, and are converted to the active agents by hydrolysis, primarily in the liver. Unlike direct vasodilators, these agents do not result in reflex sympathetic activation and can be used safely in persons with ischemic heart disease. The absence of reflex tachycardia may be due to downward resetting of the baroreceptors or to enhanced parasympathetic activity. Although converting enzyme inhibitors are most effective in conditions associated with high plasma renin activity, there is no good correlation among subjects between plasma renin activity and antihypertensive response. This effect is particularly valuable in diabetes, and these drugs are now recommended in diabetes even in the absence of hypertension. These benefits probably result from improved intrarenal hemodynamics, with decreased glomerular efferent arteriolar resistance and a resulting reduction of intraglomerular capillary pressure. Pharmacokinetics & Dosage Captopril’s pharmacokinetic parameters and dosing recommendations are set forth in Table 11–2. Peak concentrations of enalaprilat, the active metabolite of enalapril, occur 3–4 hours after dosing with enalapril. Captopril, particularly when given in high doses to patients with renal insufficiency, may cause neutropenia or proteinuria. Minor toxic effects seen more typically include altered sense of taste, allergic skin rashes, and drug fever, which may occur in up to 10% of patients. Important drug interactions include those with potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics, which can result in hyperkalemia. For effective treatment, medicines that may be expensive and sometimes produce adverse effects must be consumed daily. Thus, the physician must establish with certainty that hypertension is persistent and requires treatment and must exclude secondary causes of hypertension that might be treated by definitive surgical procedures. Persistence of hypertension, particularly in persons with mild elevation of blood pressure, should be established by finding an elevated blood pressure on at least three different office visits. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring may be the best predictor of risk and therefore of need for therapy in mild hyper-tension, and is recommended for initial evaluation of all patients in the guidelines of some countries. Once the presence of hypertension is established, the question of whether to treat and which drugs to use must be considered. The level of blood pressure, the age of the patient, the severity of organ damage (if any) due to high blood pressure, and the presence of cardiovascular risk factors all must be considered. Assessment of renal function and the presence of proteinuria are useful in antihypertensive drug selection.