
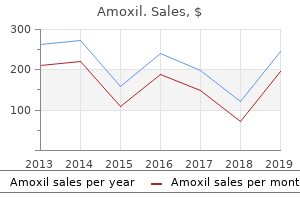
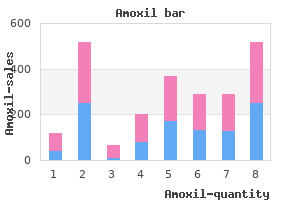
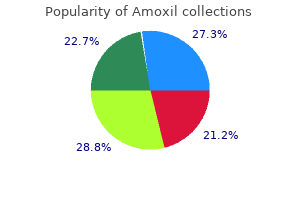
"Buy 250 mg amoxil free shipping, infection 1 year after surgery".
By: G. Tippler, M.A.S., M.D.
Medical Instructor, University of Nevada, Reno School of Medicine
Two forms of vitamin D—vitamin D (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D3 2 (ergocalciferol)—are used routinely as dietary supplements antibiotic resistant bacteria cure order genuine amoxil on-line. Additional information on preparation antibiotics for neonatal uti buy amoxil 650mg mastercard, dosage antibiotics for uti cefuroxime buy amoxil with amex, and administration is available in Table 59. P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n Vitamin D Instruct the patient to swallow oral preparations intact, without crushing or chewing. Calcitonin-Salmon Calcitonin-salmon [Miacalcin, Fortical], a form of calcitonin derived from salmon, is similar in structure to calcitonin synthesized by the human thyroid. Salmon calcitonin produces the same metabolic effects as human calcitonin but has a longer half-life and greater milligram potency. Intranasal calcitonin was removed from the Canadian market in 2013 because of an increased risk for malignancy associated with this formulation; however, it remains available in the United States. Actions Calcitonin has two principal actions: (1) it inhibits the activity of osteoclasts and thereby decreases bone resorption, and (2) it inhibits tubular resorption of calcium and thereby increases calcium excretion. As a result of decreasing bone turnover, calcitonin decreases alkaline phosphatase in blood and increases hydroxyproline in urine. Therapeutic Uses Osteoporosis Calcitonin-salmon, given by nasal spray or injection, is indicated for treatment of established postmenopausal osteoporosis—but not for prevention. The treatment program should include supplemental calcium and adequate intake of vitamin D. Paget Disease of Bone Calcitonin is helpful in moderate to severe Paget disease and is the drug of choice for rapid relief of pain associated with the disorder. Hypercalcemia Calcitonin can lower plasma calcium levels in patients with hypercalcemia secondary to hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D toxicity, and cancer. Levels of calcium (and phosphorus) are reduced owing to inhibition of bone resorption and increased renal excretion of calcium. Although calcitonin is effective against hypercalcemia, it is not a preferred treatment. Adverse Effects With intranasal dosing, nasal dryness and irritation are the most common complaints. As previously mentioned, studies demonstrating an increase in malignancies associated with nasal administration prompted withdrawal of this drug in Canada. When salmon calcitonin is taken for a year or longer, neutralizing antibodies often develop. In some patients, these antibodies bind enough calcitonin to prevent therapeutic effects. P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n Calcitonin Salmon Instruct patients using Miacalcin to prime the metered-dose pump by holding the bottle upright and depressing the two white sidearms toward the bottle 6 times, which should produce a faint initial spray. The drug is then administered by placing the nozzle in the nostril and depressing the pump handle. Teach patients how to inject calcitonin subcutaneously and instruct them to rotate sites of injection. Bisphosphonates Bisphosphonates are structural analogs of pyrophosphate, a normal constituent of bone. These drugs undergo incorporation into bone, and then inhibit bone resorption by decreasing the activity of osteoclasts.
Staff treating patients at risk of infection without an expiratory filter required protective equipment (goggles bacteria urine hpf cheap amoxil uk, N95 mask antibiotics iud buy 250mg amoxil fast delivery, gown antibiotics for cat acne cheap amoxil master card, and gloves) and scav- enger systems over the mPaw control diaphragm. A suitable filter is now available from SensorMedics and for the Vision Alpha machine. Rose L (2008) High-frequency oscillatory ventilation in adults: clinical considerations and management priorities. Dual-control or hybrid modes of ventilation can control both pressure and volume at different points in the breathing cycle (they cannot control both at the same time). They aim to provide the assured minute ventilation of volume control with the potential advantages of a decelerating inspiratory flow pattern. Dual control within a breath This principle is used by Volume-Assured Pressure Support on Bird® ven- tilators and Pressure Augmentation on Bear® ventilators (both Viasys). If the software calculates that the minimum tidal volume (or greater) will be delivered, the breath is flow cycled, that is, the equivalent of a pressure support breath. If it is calculated that the desired tidal volume will not be reached, a flow controller is activated which maintains a constant inspiratory flow until the desired tidal volume is attained. Airway pressure may rise above set ventilator pressure during this portion of the breath. There is automatic time cycling as a safety default to prevent prolonged inspiration. Dual control from breath to breath These modes measure tidal volume and adjust the pressure delivered in subsequent breaths to reach a predefined target. Pressure limited, flow cycled This is closed-loop pressure support, using tidal volume to adjust inspira- tory pressure. In subsequent breaths, pressure is increased gradually until the desired tidal volume is achieved or the set pressure limit is breached. Changes in pressure support of 1–3cmH2O per breath are then made in response to measured compliance in order to keep tidal volume constant. Pressure limited, time cycled This is closed-loop pressure control ventilation, using tidal volume to adjust inspiratory pressure. The ventilators deliver a test breath of 5–10cmH2O, determine compliance, and then gradually increase the pressure until the desired tidal volume is delivered or the set pressure limit is breached. Pressure is then adjusted (by 1–3cmH2O per breath) on the basis of measured compliance in order to keep the tidal volume constant. Automode Automode from Siemens combines the two methods of between breath dual control. If the patient is breathing spontaneously, breaths will be flow cycled, and if the patient is apnoeic, breaths will be time cycled. Problems • If there is major patient ventilator asynchrony during the test breaths calculated compliance will be erroneous. These breaths are not dual- control breaths since airway pressure is secondary to the flow delivery and respiratory mechanics, and is not controlled by the ventilator. Decelerating flow (descending ramp) Although designed to mimic a pressure-controlled breath, decelerating flow breaths cannot adjust for conditions of changing resistance. For example, in airway obstruction the slope of deceleration should be much gentler. Ventilators are unable to make these adjustments and on average airway pressures will still be slightly higher with these modes than with a true pressure-controlled breath. Sinusoidal This type of flow pattern more closely replicates the flow pattern of normal breathing. Accelerating (ascending ramp) This flow pattern tends to produce higher peak pressures and lower mean pressures, and its use is therefore limited.
Cheap amoxil 500 mg free shipping. YogaRat Yoga Towel Pro Length Review.
Regarding cancer screening tests antibiotics in meat purchase amoxil australia, the American Cancer Society and various subspecialty organizations publish var io u s r ecom m en d at ion s infection tooth extraction order amoxil australia, wh ich are oft en n o t in agr eem en t antibiotic 3142 discount 1000 mg amoxil visa. Rout ine immunizat ions include annual influenza vaccine (especially import ant in the geriat ric populat ion, since > 90% of influenza-related deat hs occur in pat ient s over 60 years), pneumo- coccal vaccin es (23-valent polysacch ar ide vaccin e an d 13-valent pn eumococcal con - jugat e vaccin e sh ou ld be given sequ ent ially), an d H er pes zost er vaccin e for pat ient s over age 60. O ffering cancer screening to older patients should consider estimated life expect ancy (t ypically at least 10 years), comorbid condit ions, and abilit y or will- ingness to undergo cancer t reat ment if a cancer is detected (eg, to tolerate a hemi- colectomy if a colon cancer is found). The physician orders a fasting glucose level, lipid panel, mammogram, colonos- copy, an d a Pap sm ear of the vagin al cu ff. Which of the followin g st at ement s is most accurate regarding the screening for this patient? I n gen er al, co lo n can cer scr een in g sh o u ld b e in it iat ed at age 6 0 b u t this patient has very sporadic care; therefore colonoscopy is reasonable. Which of the followin g is the most accurate st at ement about t his vaccine? This vaccin e is n o t r eco m m en d ed if a patient h as alr ead y d evelo p ed shingles. W hich of the following state- ments is most accurate regarding health maintenance for this individual? T h e h u m an p ap illo m a vir u s ( H P V ) vaccin e sh o u ld b e ad m in ist er ed o n ly if sh e h as a h ist ory of genit al wart s. Cervical cytology of the vaginal cuff is unnecessary when the hysterectomy was for benign indicat ions (not cervical dysplasia or cervical cancer) and wh en there is no history of abnormal Pap smears. The varicella zoster vaccine is a live attenuated vaccine, recommended for individuals aged 60 and above. It has been sh own t o great ly reduce t he inci- dence of herpes zoster (shingles) and the severity and likelihood of posther- petic neuralgia. The most common cause of mortality for adolescent females is motor vehicle accident s. He works as a computer programmer, exercises regularly at a gym, and does not smoke or use illicit drugs. His father suffered his first heart attack at age 42 and eventually died of complications of heart disease at age 49. Know the risk factors for developing coronary artery disease and know how to est imat e t he risk for coronary event s using available risk calculat ors. Be familiar with the recommendations for cholesterol screening and for the treatment of high-risk patients. Understand how the different classes of lipid-lowering agents affect lipid levels and the potential side effects of those agents. H e does not have any apparent second- ary causes of dyslipidemia, and has no signs or symptoms of vascular disease. H e does have a strong family history of hypercholesterolemia and premature death cau sed by myocar dial in far ct ion ( M I ). T h e d ecision s r egar din g the m et h od an d intensit y of lipid-lowering t herapy are based on one’s estimation of the patient’s 10-year risk of major coronary events. Becau se of h is ver y h igh lipid levels an d family history, he is a high-risk patient and, thus, should be counseled about lipid- lowering medical t h erapy. Meanwh ile, the import ance of lifest yle modification cannot be overemphasized. Because of the association of hypercholesterolemia and development of atherosclerot ic heart disease, most aut horit ies recommend routine screening of average-risk individuals at least every 5 years. One should exclude a secondary cause of lipid disorder, eit h er by clin ical or laborat ory evaluat ion. T h e most common underlying causes of dyslipidemia are hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus.
H ence antibiotics used for sinus infections uk cheap amoxil 250mg free shipping, a quick evaluat ion of t he pat ient’s respirat ory condit ion treatment for sinus infection toothache generic 650 mg amoxil with mastercard, including t he respirat ory rat e and effort ; use of accessory muscles infection zombie games buy cheap amoxil on-line, such as int ercost al and supraclavicular muscles; anxiet y; and cyanosis; may indicate mild or severe disease. Pulse oximetry and arterial blood gas studies should be ordered while informat ion is gat hered during t he hist ory and physical. Meanwhile, t he physical examinat ion should be directed at t he heart and lung evaluat ion. The lungs should be auscultated for wheezes, rhonchi, rales, or absent breath sounds. An arterial blood gas should be obtained to assess for hypoxemia, carbon dioxide retention, and acid– base status. These findings should be evaluated in the context of the physiological changes in pregnancy (see Table 15– 1). A chest radiograph should be performed rather expedi- tiously to differentiate cardiac versus pulmonary causes of hypoxemia. A large car- diac silhouette may indicate peripartum cardiomyopathy, which is treated by diuretic and inotropic therapy; pulmonary infiltrates may indicate pneumonia or pulmonary edema. A clear chest radiograph in the face of hypoxemia suggests pulmonary embo- lism, although early in the course of pneumonia, the chest x-ray may appear normal. The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism may be made presumptively on the basis of high clinical suspicion, hypoxemia, and a clear chest x-ray. In some cases, intra- ven o u s h ep a r in is in it iat ed p r o p h ylact ically wh ile co n fir m at o r y t est in g is o r d er ed. The choice of imaging modalit y will depend on physician preference, patient contraindications, and the speed at which the test can be obt ain ed. Once the diagnosis of acute thromboembolism is confirmed, the pregnant woman is usually placed on full int ravenous ant icoagulat ion t h erapy for 5 t o 7 days. After 3 months, either full heparinization or “prophylactic heparinization” doses can be utilized for the remainder of the pregnancy and for 6 weeks postpartum. Estrogen products, such as oral contraceptive agents, are relatively contraindi- cat ed in women d iagn osed wit h pu lm on ar y embolism. P r oph ylact ic ant icoagu la- tion for future pregnancies is more controversial, but is often used. The preg- nant state increases the risk fivefold due to the venous stasis with the large gravid uterus pressing on the vena cava and the hypercoagulable st ate due to the increase in clott ing factors. The risk of death is increased tenfold when pulmonary embolism is unrecognized and unt reated. In pregnancy, the diagnostic test of choice is Doppler ultrasound imaging, which usually employs a 5- to 7. This m od alit y is n ear ly as sensit ive and specific as the t ime-honored met hod of cont rast venography. Ant icoagu lat ion t h erapy is the same as pulmonar y embolism t r eat ment wit h full int ravenous doses for 5 to 7 days, followed by subcut aneous t herapy for at least 3 months after the acute event. After 3 months, either full or prophylactic heparin doses can be utilized for the remainder of the pregnancy and for 6 weeks postpartum. Patients who have additional risk factors for thromboembolism out- side of pregnancy may need long-term ant icoagulat ion. This occur s wh en amn iot ic fluid ent er s the mat er- nal circulation and subsequently causes obstruction and vasoconstriction of the pulmonary vessels due to fetal debris and vasoactive substances in the fluid. The patient may present with sudden dyspnea, hypoxia, hypotension, and coagulop- athy. The rate of maternal mort alit y ranges from 20% to 60% and is t ypically due to cardiovascular collapse.